The goal of the NanoRef programme, involving multiple partners (LP-Cnam, INM, LPUB, Institut Fresnel, Novasic and LNE), is to develop aglass roughness standard with a quasi-continuum spatial frequency spectrum and to define the appropriate machining and polishing processes.
The results of the NanoRef programme will be of interest in numerous domains including tribology, optoelectronics, automotive, precision mechanics, semi-conductors and metrology.
In this context, the LNE (French National Metrology Institute) used an AFM to analyze the roughness of strips of glass subjected to hydrofluoric acid attacks of different durations.
Courtesy of LNE (French National Metrology Institute)
Mountains® tools used
-
Analysis of surface evolution over time
A movie of the series of 25 topography images shows evolution of pitting on the glass surface caused by acid attack.

-
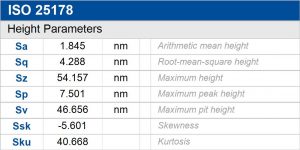
ISO 25178 height parameters
Statistics, including 3D parameter tables, were generated to track changes to the surface after the attack.
Instrument & software used
Atomic force microscope (AFM) + MountainsSPIP® software